Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Topic Contents
- General Information About Nasopharyngeal Cancer
- Stages of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
- Treatment Option Overview
- Treatment of Stage I Nasopharyngeal Cancer
- Treatment of Stage II, III, and IVA Nasopharyngeal Cancer
- Treatment of Stage IVB and Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Cancer
- To Learn More About Nasopharyngeal Cancer
- About This PDQ Summary
Nasopharyngeal Cancer Treatment (PDQ®): Treatment - Patient Information [NCI]
This information is produced and provided by the National Cancer Institute (NCI). The information in this topic may have changed since it was written. For the most current information, contact the National Cancer Institute via the Internet web site at http://cancer.gov or call 1-800-4-CANCER.
General Information About Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a type of head and neck cancer that starts in the tissues of the nasopharynx.
The pharynx is a hollow tube in the neck about 5 inches long that is made up of three parts:
- The nasopharynx is the upper part of the pharynx, located behind the nose. The nostrils are connected to the nasopharynx. Openings on each side of the nasopharynx lead to the ears.
- The oropharynx is the middle part, located beneath the nasopharynx.
- The hypopharynx is the lowermost part of the pharynx, opening up to both the trachea (windpipe) and esophagus.
When we breathe or swallow, the pharynx acts as a passageway for air to reach the lungs and food to reach the stomach. Nasopharyngeal cancer commonly begins in the squamous cells that line the nasopharynx.
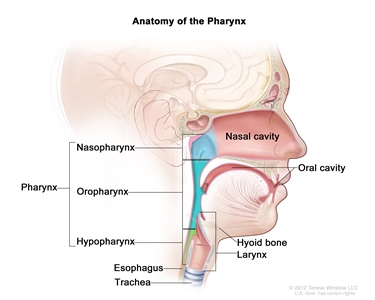
Anatomy of the pharynx. The pharynx is a hollow, muscular tube inside the neck that starts behind the nose and opens into the larynx and esophagus. The three parts of the pharynx are the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx.
Being exposed to the Epstein-Barr virus, your ancestry, and where you live can affect the risk of nasopharyngeal cancer.
Nasopharyngeal cancer is caused by certain changes in how nasopharyngeal cells function, especially how they grow and divide into new cells. There are many risk factors for nasopharyngeal cancer, but many do not directly cause cancer. Instead, they increase the chance of DNA damage in cells that may lead to nasopharyngeal cancer. Learn more about how cancer develops at What Is Cancer?
A risk factor is anything that increases a person's chance of getting a disease. Some risk factors for nasopharyngeal cancer, like tobacco use, can be changed. Risk factors also include things you cannot change, like your family history. Learning about risk factors for nasopharyngeal cancer can help you make choices that might prevent or lower your risk of getting it.
Risk factors for nasopharyngeal cancer include:
- being infected with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
- living in or having ancestry in certain parts of Asia, North Africa, and the Arctic
- having a family member with nasopharyngeal cancer
- using tobacco or breathing in secondhand smoke
- frequent and heavy alcohol use
- having a diet high in salt-cured fish and meats because these foods may contain cancer-causing chemicals, such as nitrosamine
Nasopharyngeal cancer can occur at any age. In areas where the disease is not common, it is more likely to be diagnosed in people who are older than 50 years. In high-risk areas, younger people are more likely to be affected. Men tend to develop nasopharyngeal cancer more often than women. In rare cases, human papillomavirus (HPV), especially HPV type 16, has been linked to nasopharyngeal cancer. Learn about HPV and Cancer.
Signs and symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer include trouble breathing, speaking, or hearing.
The signs and symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer can vary from person to person. Early signs and symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer may include:
- a lump in the neck
- pain, pulsing, or ringing in the ear
- trouble hearing
- a sore throat
- stuffy nose
- nosebleeds
Signs and symptoms of advanced nasopharyngeal cancer (nasopharyngeal cancer that has spread to other parts of the body) may include symptoms of early-stage nasopharyngeal cancer and:
- misalignment of the eyes (strabismus)
- double vision
- headaches
- facial numbness
- facial weakness
These problems may be caused by conditions other than nasopharyngeal cancer. Check with your doctor if you have any of these problems to find out the cause and begin treatment, if needed.
Tests that examine the nose, throat, and nearby organs are used to diagnose and stage nasopharyngeal cancer.
If you have symptoms that suggest nasopharyngeal cancer, your doctor will need to find out if these are due to cancer or another problem. They will ask when the symptoms started and how often you have been having them. They will also ask about your personal and family health history and do a physical exam. Based on these results, the doctor may recommend other tests. If you are diagnosed with nasopharyngeal cancer, the results of these tests will help you and your doctor plan treatment.
The following tests and procedures are used to diagnose and stage nasopharyngeal cancer:
- Nasopharyngoscopy with biopsy is a procedure to examine the inside of the nose and back of the throat. The doctor inserts a nasopharyngoscope (a thin, flexible lighted tube) in the nose and advances it to the back of the throat to check for abnormal areas. The nasopharyngoscope may have a tool to remove a sample of cells or tissue (biopsy) so a pathologist can view it under a microscope to check for signs of cancer. Learn about the type of information that can be found in a pathologist's report about the cells or tissue removed during a biopsy at Pathology Reports.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. This procedure is also called nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI).
- PET-CT scan combines pictures from a positron emission tomography (PET) scan and a computed tomography (CT) scan. The PET and CT scans are done at the same time on the same machine. The combined pictures make a more detailed picture than either test would make by itself.
- For the PET scan, a small amount of radioactive glucose (sugar) is injected into a vein. The scanner rotates around the body and makes a picture of where glucose is being used in the body. Because cancer cells often take up more glucose than normal cells, the pictures can be used to find cancer cells in the body.
- For the CT scan, a series of detailed x-ray pictures of areas inside the body is taken from different angles. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly.
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) test is a blood test to check for antibodies and DNA markers that are found in the blood of people who have been infected with EBV.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) test is a laboratory test used to check a sample of tissue for certain types of HPV infection. An HPV test is usually done if the EBV test is negative. This is because in rare cases, HPV can cause nasopharyngeal cancer.
- A neurological exam uses a series of questions and tests to check brain, spinal cord, and nerve function. The exam checks your mental status, coordination, and ability to walk normally, and how well the muscles, senses, and reflexes work. This may also be called a neuro exam or a neurologic exam.
- A hearing test checks your ability to hear soft and loud sounds and low- and high-pitched sounds. Each ear is checked separately. This test is done because nasopharyngeal cancer and its treatment can affect hearing. Hearing tests are usually done before, during, and after treatment.
- Blood chemistry study is a laboratory test in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amounts of certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body. An unusual (higher or lower than normal) amount of a substance can be a sign of disease.
- Complete blood count (CBC) is a laboratory test in which a sample of blood is drawn and checked for:
- the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
- the amount of hemoglobin (the substance in the blood that carries oxygen) in the red blood cells
- the amount of hematocrit (whole blood that is made up of red blood cells)
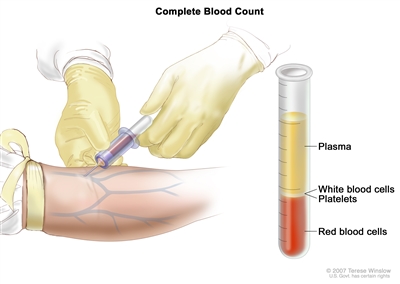
Complete blood count (CBC). Blood is collected by inserting a needle into a vein and allowing the blood to flow into a tube. The blood sample is sent to the laboratory and the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are counted. The CBC is used to test for, diagnose, and monitor many different conditions.
Some people may decide to get a second opinion.
You may want to get a second opinion to confirm your nasopharyngeal cancer diagnosis and treatment plan. If you seek a second opinion, you will need to get medical test results and reports from the first doctor to share with the second doctor. The second doctor will review the pathology report, slides, and scans. They may agree with the first doctor, suggest changes or another treatment approach, or provide more information about your cancer.
Learn more about choosing a doctor and getting a second opinion at Finding Cancer Care. You can contact NCI's Cancer Information Service via chat, email, or phone (both in English and Spanish) for help finding a doctor, hospital, or getting a second opinion. For questions you might want to ask at your appointments, visit Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Cancer.
Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
The prognosis and treatment options depend on:
- the size of the tumor
- the stage of the cancer, including whether cancer has spread to one or more lymph nodes in the neck
- whether there are high levels of EBV antibodies and EBV-DNA markers in the blood before and after treatment
Stages of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Cancer stage describes the extent of cancer in the body.
Cancer stage describes the extent of cancer in the body, such as the size of the tumor, whether it has spread, and how far it has spread from where it first formed. Knowing the cancer stage helps plan treatment.
There are several staging systems for cancer that describe the extent of the cancer. Nasopharyngeal cancer staging usually uses the TNM staging system. The cancer may be described by this staging system in your pathology report. Based on the TNM results, a stage (I, II, III, or IV, also written as 1, 2, 3, or 4) is assigned to the cancer. When talking to you about your diagnosis, your doctor may describe the cancer as one of these stages.
Learn more about Cancer Staging.
The following stages are used for nasopharyngeal cancer:
Stage 0 (also called carcinoma in situ of the nasopharynx)
In stage 0, abnormal cells are found in the lining of the nasopharynx. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue.
Stage I (also called stage 1) nasopharyngeal cancer
In stage I, cancer has formed, and the cancer:
- is found in the nasopharynx only; or
- has spread from the nasopharynx to the oropharynx and/or to the nasal cavity.
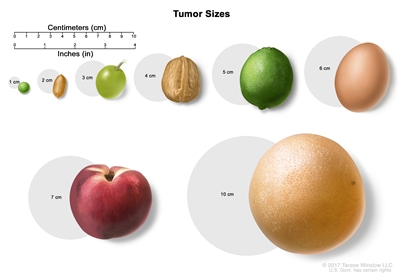
Tumor sizes are often measured in centimeters (cm) or inches. Common food items that can be used to show tumor size in cm include: a pea (1 cm), a peanut (2 cm), a grape (3 cm), a walnut (4 cm), a lime (5 cm or 2 inches), an egg (6 cm), a peach (7 cm), and a grapefruit (10 cm or 4 inches).
Stage II (also called stage 2) nasopharyngeal cancer
In stage II, one of the following is true:
- Cancer has spread to one or more lymph nodes on one side of the neck and/or to one or more lymph nodes on one or both sides of the back of the throat. The affected lymph nodes are 6 centimeters or smaller. Cancer is found:
- in the nasopharynx only or has spread from the nasopharynx to the oropharynx and/or to the nasal cavity; or
- only in the lymph nodes in the neck. The cancer cells in the lymph nodes are infected with Epstein-Barr virus (a virus linked to nasopharyngeal cancer).
- Cancer has spread to the parapharyngeal space and/or nearby muscles. Cancer may have also spread to one or more lymph nodes on one side of the neck and/or to one or more lymph nodes on one or both sides of the back of the throat. The affected lymph nodes are 6 centimeters or smaller.
Stage III (also called stage 3) nasopharyngeal cancer
In stage III, one of the following is true:
- Cancer has spread to one or more lymph nodes on both sides of the neck. The affected lymph nodes are 6 centimeters or smaller. Cancer is found:
- in the nasopharynx only or has spread from the nasopharynx to the oropharynx and/or to the nasal cavity; or
- only in the lymph nodes in the neck. The cancer cells in the lymph nodes are infected with Epstein-Barr virus (a virus linked to nasopharyngeal cancer).
- Cancer has spread to the parapharyngeal space and/or nearby muscles. Cancer has also spread to one or more lymph nodes on both sides of the neck. The affected lymph nodes are 6 centimeters or smaller.
- Cancer has spread to the bones at the bottom of the skull, the bones in the neck, jaw muscles, and/or the sinuses around the nose and eyes. Cancer may have also spread to one or more lymph nodes on one or both sides of the neck and/or the back of the throat. The affected lymph nodes are 6 centimeters or smaller.
Stage IV (also called stage 4) nasopharyngeal cancer
Stage IV is divided into stages IVA and IVB.
- In stage IVA:
- Cancer has spread to the brain, the cranial nerves, the hypopharynx, the salivary gland in the front of the ear, the bone around the eye, and/or the soft tissues of the jaw. Cancer may have also spread to one or more lymph nodes on one or both sides of the neck and/or the back of the throat. The affected lymph nodes are 6 centimeters or smaller; or
- Cancer has spread to one or more lymph nodes on one or both sides of the neck. The affected lymph nodes are larger than 6 centimeters and/or are found in the lowest part of the neck.
- In stage IVB: Cancer has spread beyond the lymph nodes in the neck to distant lymph nodes, such as those between the lungs, below the collarbone, or in the armpit or groin, or to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver.
Stage IV nasopharyngeal cancer is also called metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer. Metastatic cancer happens when cancer cells travel through the lymphatic system or blood and form tumors in other parts of the body. The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if nasopharyngeal cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually nasopharyngeal cancer cells. The disease is called metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer, not lung cancer. Learn more in Metastatic Cancer: When Cancer Spreads.
Nasopharyngeal cancer can recur (come back) after it has been treated.
Recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer is cancer that has come back after it has been treated. If nasopharyngeal cancer comes back, it may come back in the nasopharynx, lymph nodes, or other parts of the body, such as the lungs, bone, or liver. Tests will help determine where in the body the cancer has returned. The type of treatment that you have for recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer will depend on where it has come back.
Learn more in Recurrent Cancer: When Cancer Comes Back. Information to help you cope and talk with your health care team can be found in the booklet When Cancer Returns.
Treatment Option Overview
There are different types of treatment for people with nasopharyngeal cancer.
Different types of treatments are available for nasopharyngeal cancer. You and your cancer care team will work together to decide your treatment plan, which may include more than one type of treatment. Many factors will be considered, such as the stage of the cancer, your overall health, and your preferences. Your plan will include information about your cancer, the goals of treatment, your treatment options and the possible side effects, and the expected length of treatment.
Talking with your cancer care team before treatment begins about what to expect will be helpful. You'll want to learn what you need to do before treatment begins, how you'll feel while going through it, and what kind of help you will need. Learn more at Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Your Treatment.
The following types of treatment are used:
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing by damaging their DNA. The way radiation therapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer. External and internal radiation therapy are used to treat nasopharyngeal cancer.
- External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the area of the body with cancer.
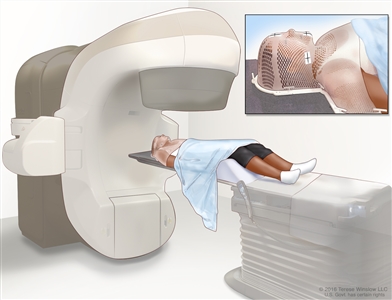
External-beam radiation therapy of the head and neck. A machine is used to aim high-energy radiation at the cancer. The machine can rotate around the patient, delivering radiation from many different angles to provide highly conformal treatment. A mesh mask helps keep the patient's head and neck from moving during treatment. Small ink marks are put on the mask. The ink marks are used to line up the radiation machine in the same position before each treatment.Certain ways of giving radiation therapy can help keep radiation from damaging nearby healthy tissue. These include:
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): IMRT is a type of 3-dimensional (3-D) radiation therapy that uses a computer to make pictures of the size and shape of the tumor. Thin beams of radiation of different intensities (strengths) are aimed at the tumor from many angles. Compared to standard radiation therapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy may be less likely to cause dry mouth. You will likely have treatment once a day, Monday through Friday, for about 6 to 7 weeks.
- Stereotactic radiation therapy: Stereotactic radiation therapy also uses a computer to make detailed images of the tumor. Thin beams of radiation are aimed at the tumor from different angles. High-dose radiation is given in one to five sessions spread over several days. This procedure is also called stereotactic external-beam radiation and stereotaxic radiation therapy.
External radiation therapy to the thyroid or the pituitary gland may change the way the thyroid gland works. A blood test to check the thyroid hormone level in the blood is done before and after therapy to make sure the thyroid gland is working properly. It is also important that a dentist check your teeth, gums, and mouth, and fix any existing problems before radiation therapy begins.
- Internal radiation therapy (also called brachytherapy) uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters that are placed directly into or near the cancer. In some cases, it may be used with external radiation therapy to deliver an extra dose of radiation directly to the tumor. Learn more about Brachytherapy to Treat Cancer.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (also called chemo) uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. Chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal cancer is usually systemic, meaning it is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle. When given this way, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body.
Chemotherapy drugs used to treat nasopharyngeal cancer include:
- carboplatin
- cisplatin
- docetaxel
- fluorouracil
- gemcitabine
Combinations of these drugs may be used. Other chemotherapy drugs not listed here may also be used.
Chemotherapy may be combined with other types of treatment, such as radiation therapy.
To learn more about how chemotherapy works, how it is given, common side effects, and more, visit Chemotherapy to Treat Cancer and Chemotherapy and You: Support for People With Cancer.
Surgery
Surgery to remove the tumor is sometimes used for nasopharyngeal cancer that does not respond to radiation therapy. If cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, the doctor may remove lymph nodes and other tissues in the neck.
Learn more about Surgery to Treat Cancer.
Treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer may cause side effects.
For information about side effects caused by treatment for cancer, visit our Side Effects page.
Side effects from cancer treatment that begin after treatment and continue for months or years are called late effects. Late effects of nasopharyngeal cancer treatment may include:
- chronic dry mouth
- dental and oral complications
- hearing loss
- vision loss
- difficulty swallowing
- lockjaw
- problems with the thyroid and pituitary gland
- damage to nerves in the brain
- changes in mood, feelings, thinking, learning, or memory
Some late effects may be treated or controlled. It is important to talk with your doctor about possible late effects caused by some treatments.
New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
For some people, joining a clinical trial may be an option. There are different types of clinical trials for people with cancer. For example, a treatment trial tests new treatments or new ways of using current treatments. Supportive care and palliative care trials look at ways to improve quality of life, especially for those who have side effects from cancer and its treatment.
You can use the clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials accepting participants. The search allows you to filter trials based on the type of cancer, your age, and where the trials are being done. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Learn more about clinical trials, including how to find and join one, at Clinical Trials Information for Patients and Caregivers.
Follow-up care may be needed.
As you go through treatment, you will have follow-up tests or check-ups. Some tests that were done to diagnose or stage the cancer may be repeated to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred (come back).
After treatment is complete, it is important to have head and neck exams to look for signs that the cancer has come back.
Treatment of Stage I Nasopharyngeal Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I nasopharyngeal cancer is usually radiation therapy to the tumor and lymph nodes in the neck.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treatment of Stage II, III, and IVA Nasopharyngeal Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage II, III, and IVA (nonmetastatic) nasopharyngeal cancer may include:
- radiation therapy to the tumor and lymph nodes in the neck
- chemotherapy given with radiation therapy, followed by more chemotherapy
- chemotherapy followed by more chemotherapy given with radiation therapy
- chemotherapy followed by radiation therapy (under study)
- surgery to remove lymph nodes if they still contain cancer cells after initial treatment
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treatment of Stage IVB and Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IVB (metastatic) or recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer may include:
- intensity-modulated radiation therapy, stereotactic radiation therapy, or internal radiation therapy
- surgery
- chemotherapy
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
To Learn More About Nasopharyngeal Cancer
For more information from the National Cancer Institute about nasopharyngeal cancer, visit:
- Head and Neck Cancer Home Page
- Oral Cavity and Nasopharyngeal Cancers Screening
- Oral Complications of Cancer Therapies
- Drugs Approved for Head and Neck Cancer
- Head and Neck Cancers
- Tobacco (includes help quitting)
For general cancer information and other resources from the National Cancer Institute, visit:
About This PDQ Summary
About PDQ
Physician Data Query (PDQ) is the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) comprehensive cancer information database. The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language. The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in Spanish.
PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). NIH is the federal government's center of biomedical research. The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH.
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of adult nasopharyngeal cancer. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Reviewers and Updates
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Updated") is the date of the most recent change.
The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board.
Clinical Trial Information
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another. Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients. During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard." Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Clinical trials can be found online at NCI's website. For more information, call the Cancer Information Service (CIS), NCI's contact center, at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as "NCI's PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: [include excerpt from the summary]."
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Nasopharyngeal Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/patient/adult/nasopharyngeal-treatment-pdq. Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>. [PMID: 26389409]
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the Managing Cancer Care page.
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer.gov through the website's E-mail Us.
Last Revised: 2024-04-26
If you want to know more about cancer and how it is treated, or if you wish to know about clinical trials for your type of cancer, you can call the NCI's Cancer Information Service at 1-800-422-6237, toll free. A trained information specialist can talk with you and answer your questions.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Ignite Healthwise, LLC.


